Online shoppers look for personalized experiences. In fact, 71% of consumers now expect tailored interactions when shopping, which puts customization and personalization at the top of the priority list for ensuring e-commerce success.
While often mentioned together, personalization and customization serve different purposes in e-commerce. Personalization uses customer data to automatically tailor experiences, while customization puts control directly in customers’ hands to modify products.
Today, you’ll learn how these approaches differ, strategies for implementation, when to use each method, and real examples of stores successfully using both to boost sales and customer satisfaction.
How are personalization and customization in e-commerce different?
What is personalization in e-commerce?
This term refers to the act of tailoring shopping experiences based on customer data. When you see “You might also like” product suggestions or receive emails featuring items related to your browsing history, you’re experiencing personalization.
Common examples include:
- Product recommendations based on past purchases
- Cross-sells and up-sells on product pages (“Frequently bought together”)
- Segmented email campaigns targeting specific customer groups (new customers, repeat buyers)
- Location-based product showcasing (winter coats for northern customers)
- Personalized homepage content displaying recently viewed items
These are all great things to have in your store, but you need to keep in mind that implementing personalization requires substantial resources. Most of all, you need reliable data collection systems that track user behavior and analytics tools to process and interpret all that information. Once you have this, you can use AI or machine learning algorithms to make predictions about future purchases.
However, with good personalization comes great responsibility. If you are using and integrating these systems, you need to address privacy concerns through transparent data policies, secure storage practices, and compliance with regulations like GDPR.
What is customization in e-commerce?
Unlike personalization, customization puts the control directly in customers’ hands. It allows shoppers to modify products according to their preferences before purchasing.
Examples of customization include:
- Adding engravings to jewelry or watches
- Uploading photos to be printed on mugs, T-shirts, or phone cases
- Selecting fabric types, colors, or patterns for clothing
- Building custom computers with specific components
- Choosing ingredients for subscription food boxes
However, to make this work, you need good product configuration tools that present options clearly and don’t bug out mid-process.
Ideally, there should also be visual previews showing changes in real time and pricing calculators that adjust costs based on selections. This helps people see the end result and price accordingly.
You also have to incorporate inventory systems that track component availability and production workflows that accommodate custom orders.
Key differences between customization and personalization
While people often confuse them, customization and personalization function in fundamentally different ways:
| Aspect | Personalization | Customization |
| Control | System-driven: Algorithms automatically adapt content based on user data | User-driven: Customers manually select options and preferences |
| Data Processing | Complex: Requires extensive data collection and AI/ML analysis to predict preferences | Simple: Users directly state what they want through selections |
| Implementation | Dynamic: Constantly adjusts in real time based on ongoing interactions | Static: Remains unchanged until the user makes manual modifications |
| Resource Needs | High: Requires sophisticated technology infrastructure and data science expertise | Moderate: Mainly needs user interface controls and preference systems |
| Customer Awareness | Often invisible: Changes happen behind the scenes | Explicit: Customers actively engage with customization options |
| Timing | Proactive: Anticipates needs before customers express them | Reactive: Responds to specific customer choices |
When to use personalization and when to use customization in e-commerce
| Personalization | Customization | Best used together |
| For real-time content adaptation | When customers want direct control | Building comprehensive e-commerce platforms |
| When targeting specific customer segments | For physical product modifications | Creating multi-channel customer experiences |
| For automated product recommendations | When creating made-to-order items | Offering both standard and custom products |
| When implementing dynamic pricing | For specialized or niche products | |
| For tailoring email marketing campaigns |
In short, personalization works best for data-driven, automated experiences, while customization shines when customers need direct control over product features. Many successful businesses implement both strategies to maximize customer satisfaction and engagement.
Examples of customization in e-commerce
Customization in e-commerce gives customers control over product specifications, creating unique items tailored to their needs. Let’s explore how field-based customization works in practice with WooCommerce stores.
Field-based customization options
Modern e-commerce customization goes far beyond simple drop-down menus. Store owners can now offer sophisticated options:
- Conditional form fields create dynamic shopping experiences by showing or hiding options based on previous selections. For example, when a customer selects “Add monogramming”, a text field appears allowing them to write the letters they want; otherwise, it’s hidden. This keeps product pages clean and relevant because only what’s needed is displayed.
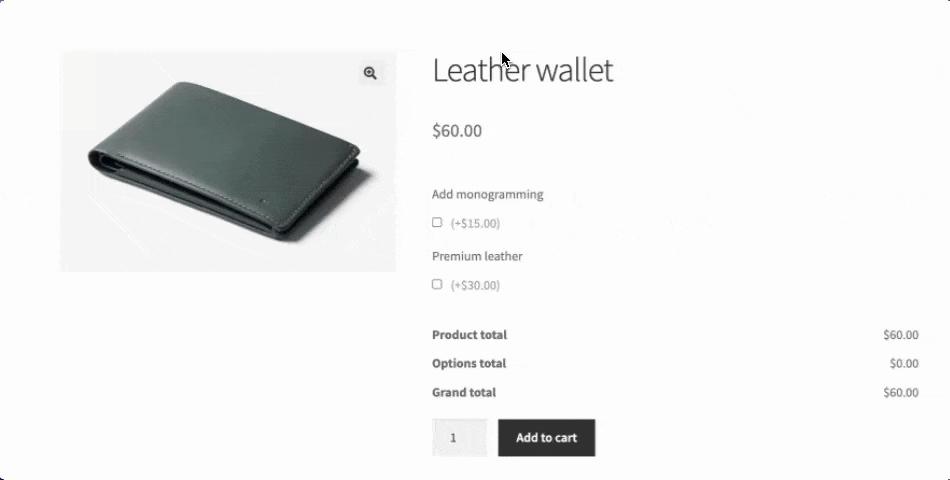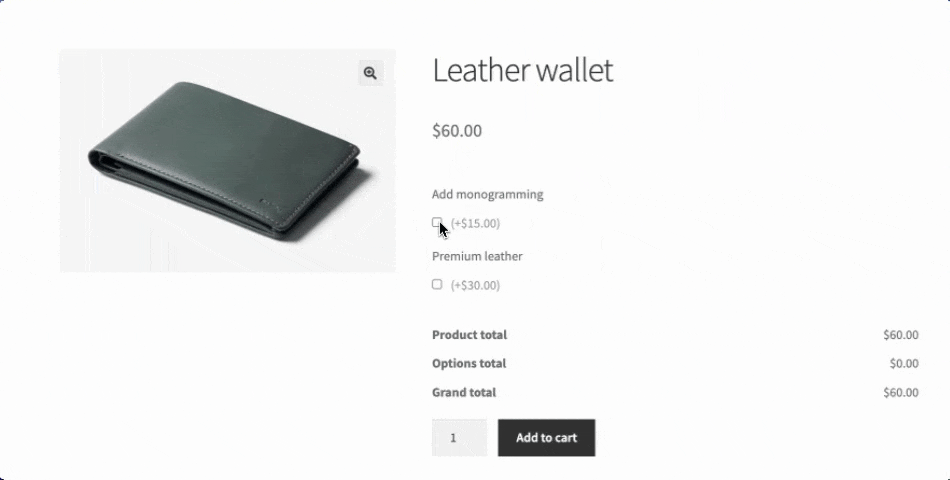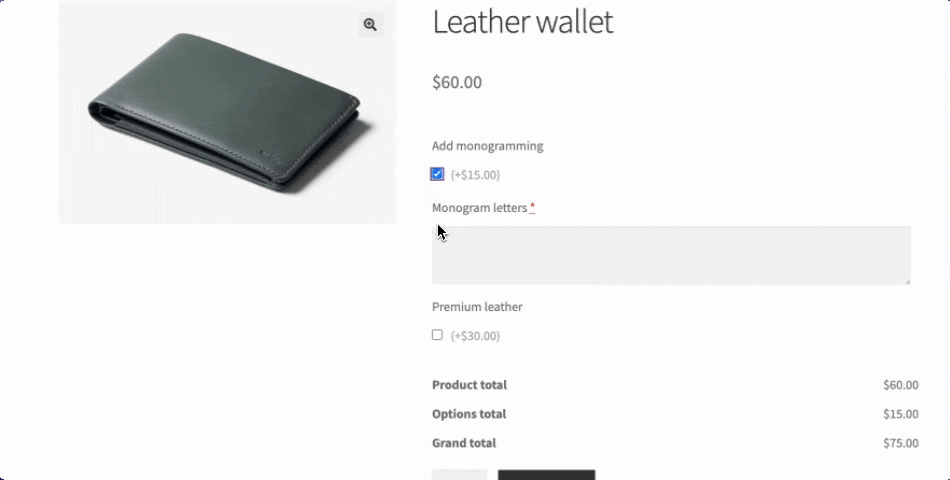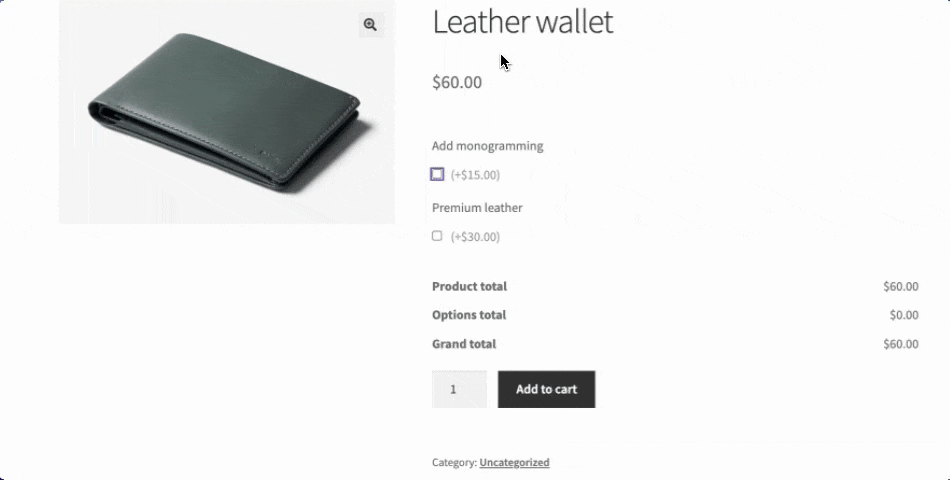
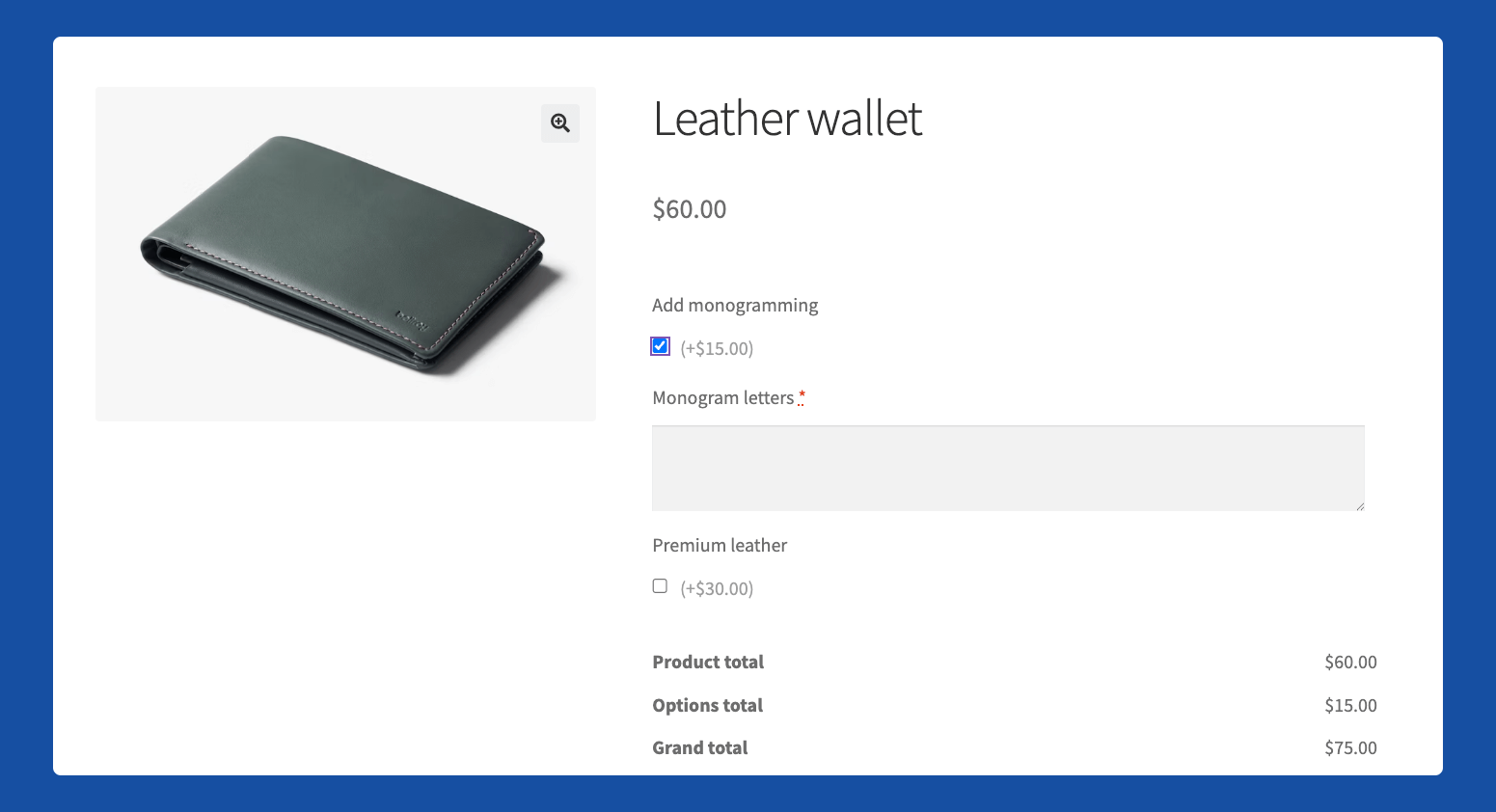
- Price calculation rules automatically adjust the final cost based on customer selections. Adding monogramming to a leather wallet might add $15, while selecting premium leather might add $30. These dynamic pricing models ensure customers see exactly how their choices affect the final price.
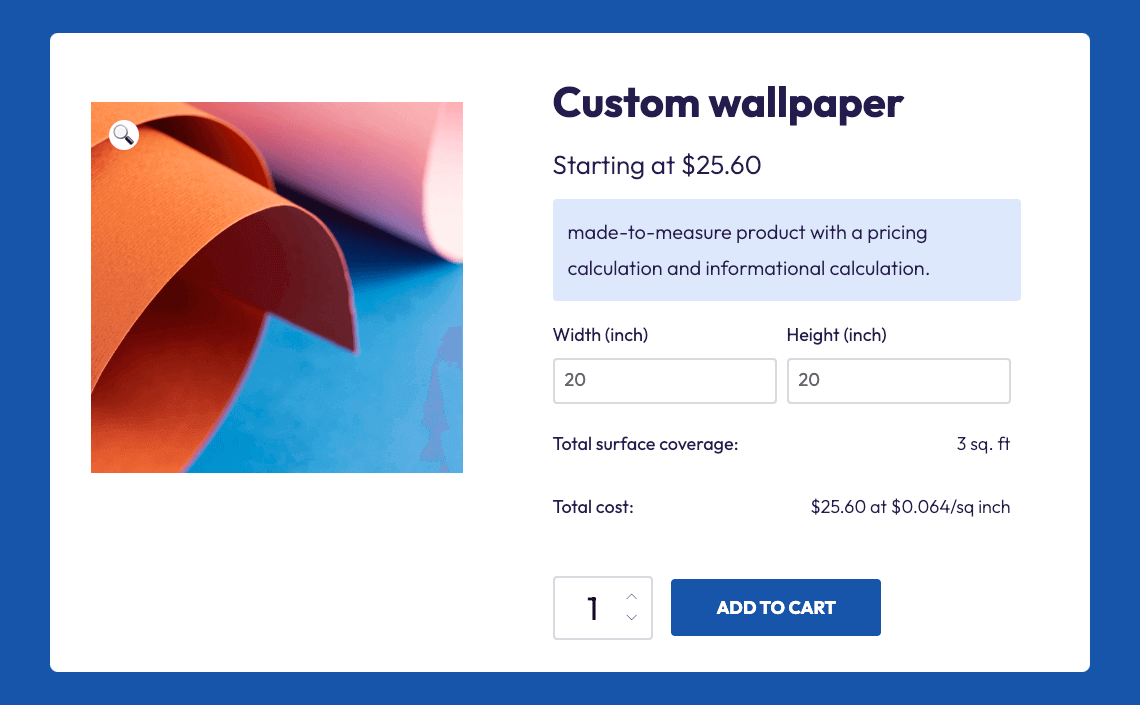
- Required fields ensure customers provide all necessary information. For custom furniture, required fields might collect dimensions, material preferences, and delivery details, preventing incomplete orders that cause production delays.
- Multi-field configuration simplifies complex product customization by integrating different field types for the different steps. In the example below, you can see that the alignment choice visually shows what the product would look like, the line colors both come with color swatches, and the text font is a drop-down menu.
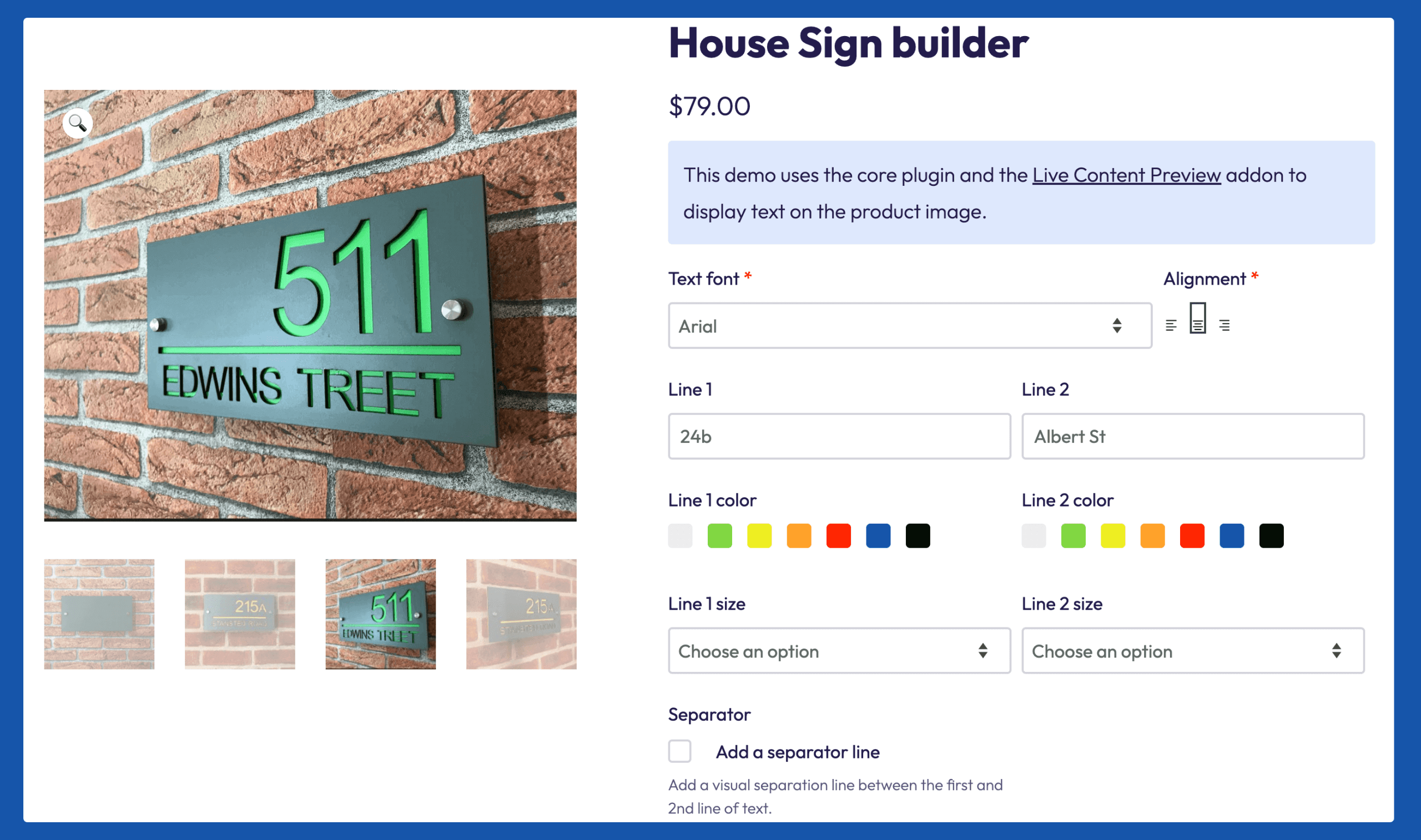
How to include customization options in WooCommerce
WooCommerce, despite being one of the largest e-commerce platforms, has limited customization capabilities. So, if you want to go beyond the basics, you need a dedicated plugin. Advanced Product Fields for WooCommerce (APF) makes adding customization options straightforward without requiring technical expertise.
Here’s how you can set up a custom engraving option for a ring using APF:
- Install and activate the Advanced Product Fields plugin.
- Edit your product and navigate to the “Custom Fields” tab.
- Add a radio button field labeled “Add engraving” with Yes/No options and assign a price adjustment for the engraving service.
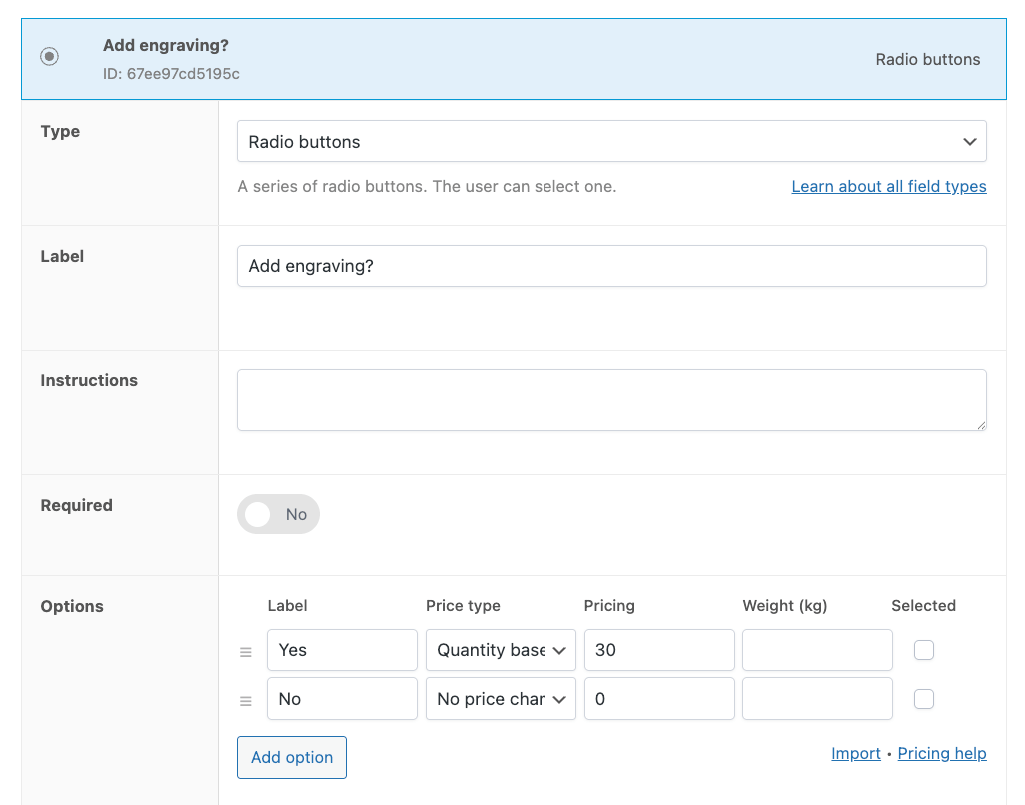
- Create a text field for the engraving message.
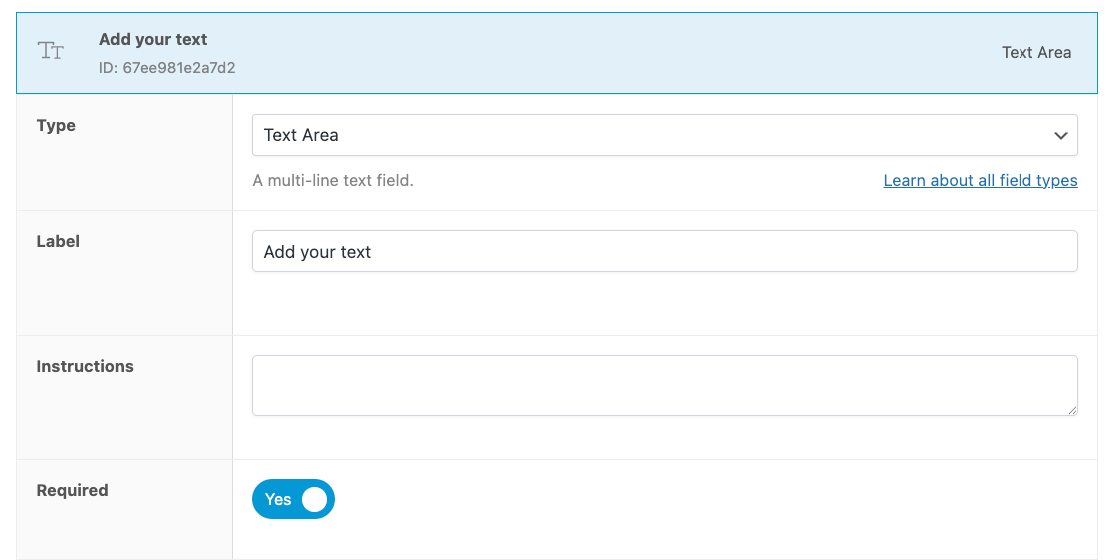
- Set up conditional logic so the text field appears only when “Add engraving” is checked.
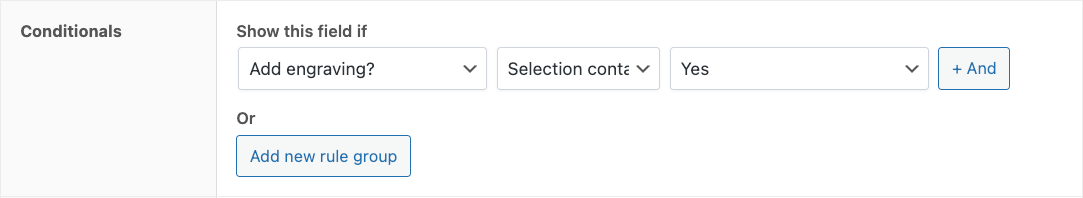
- Save and test on the frontend.
When customers check “Add engraving,” the text field automatically appears, allowing them to enter their message. This seamless experience keeps the product page uncluttered while offering valuable customization options.
If you prefer, you can even choose to have the price per character, so the longer the engraving, the higher the add-on cost.
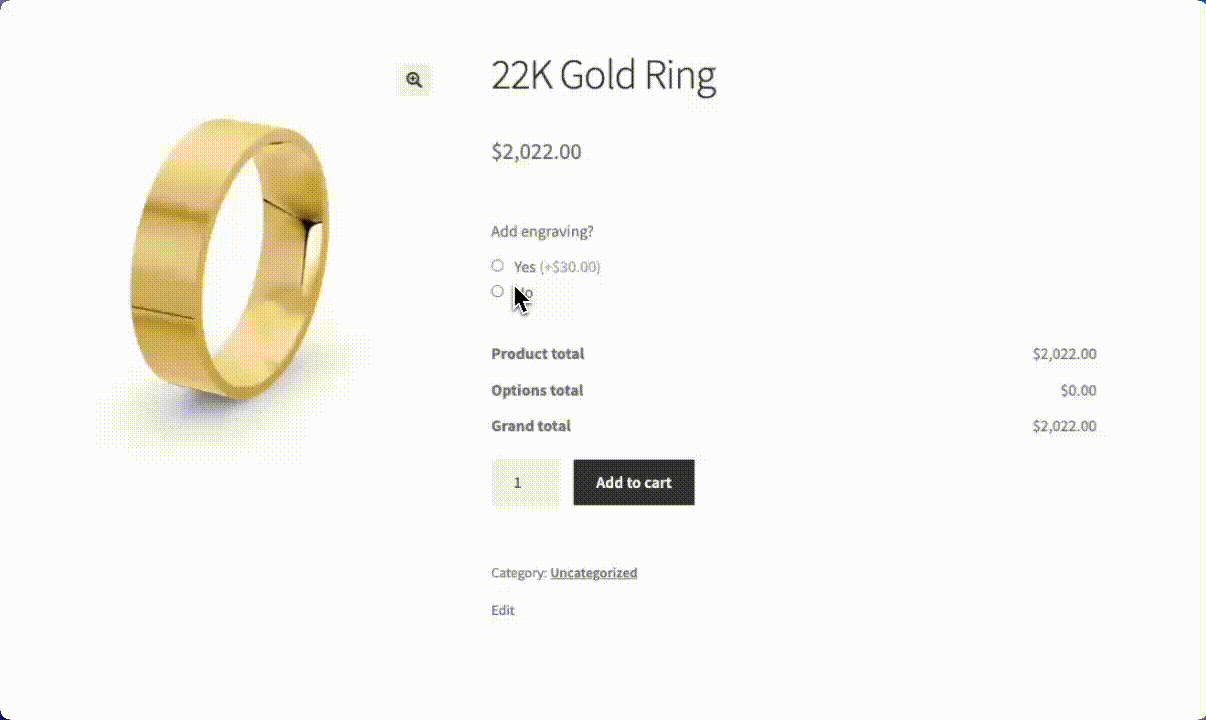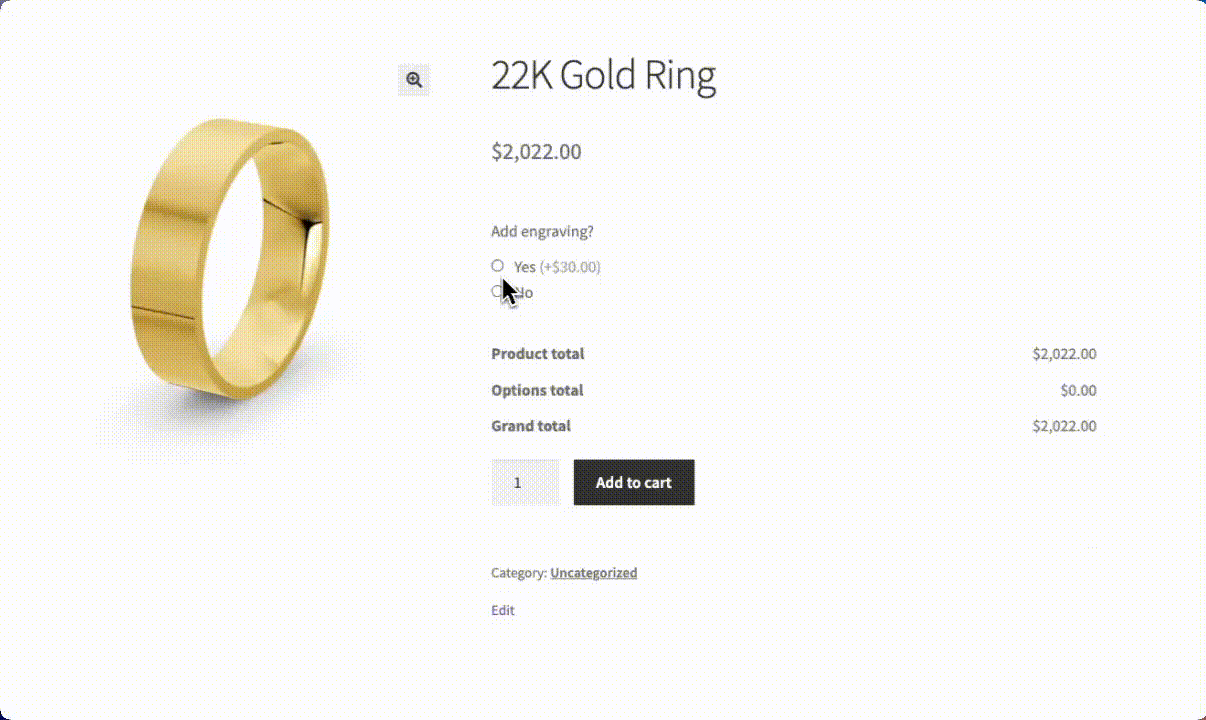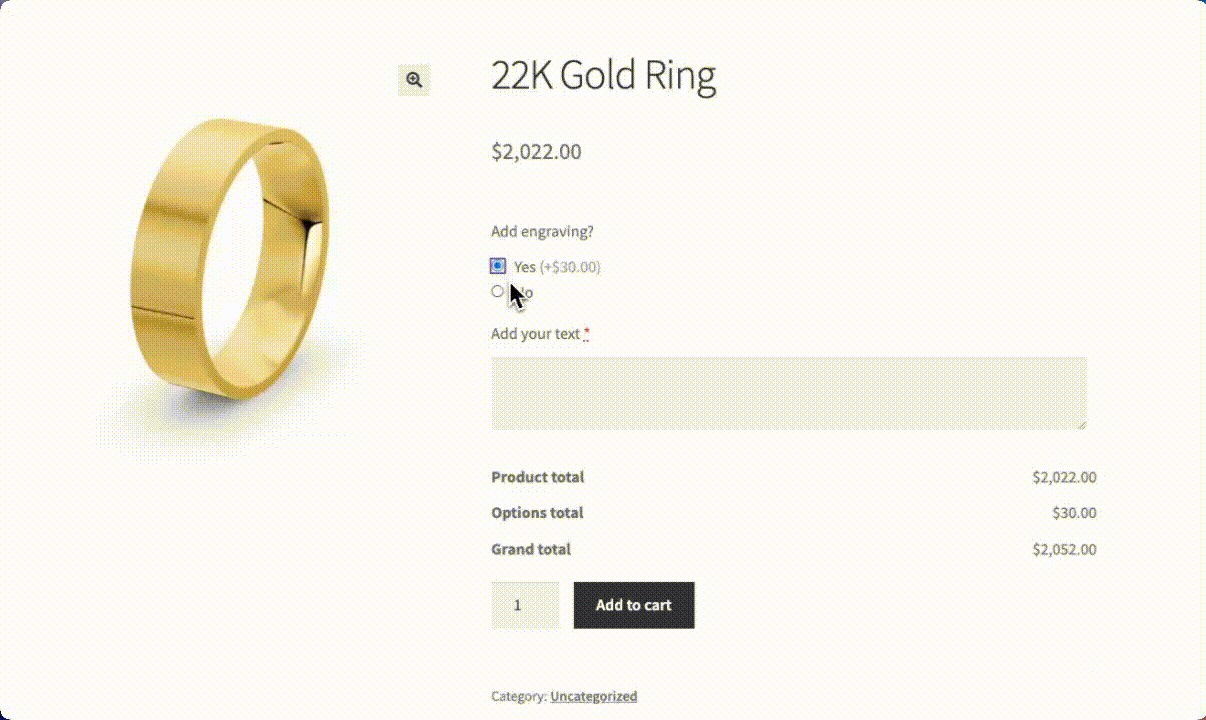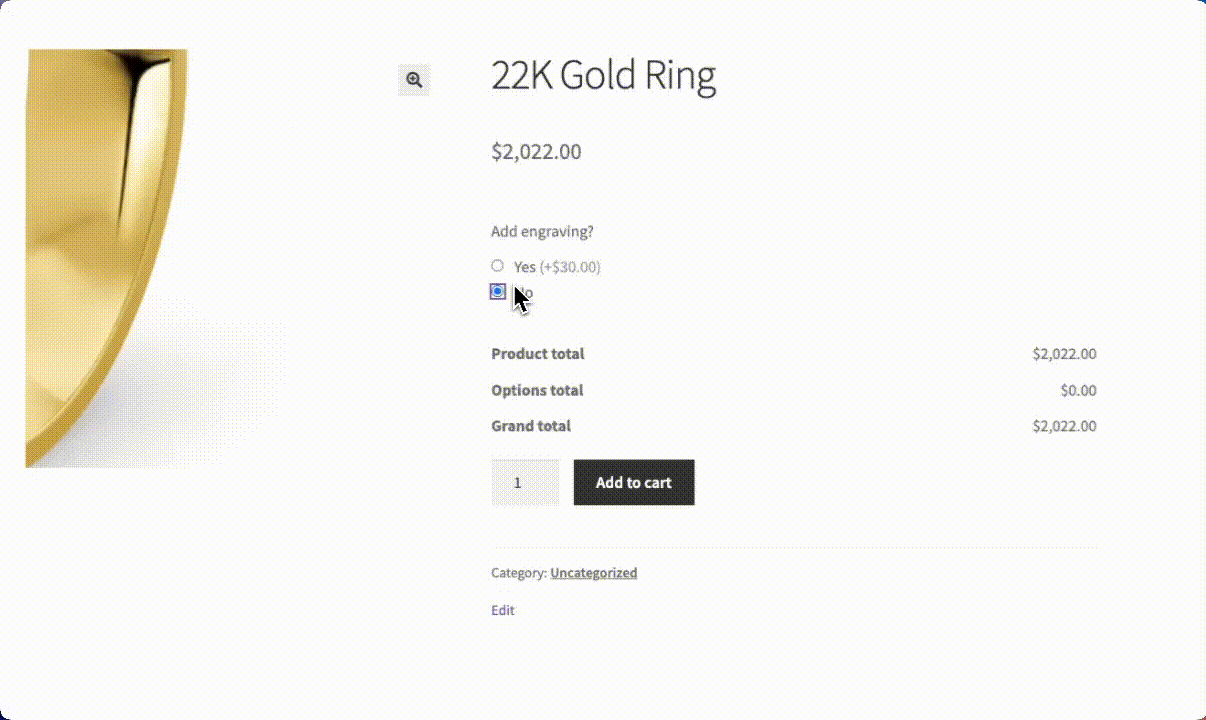
Beyond engraving, the same approach works for numerous customization scenarios:
- Cake builders with topping selection
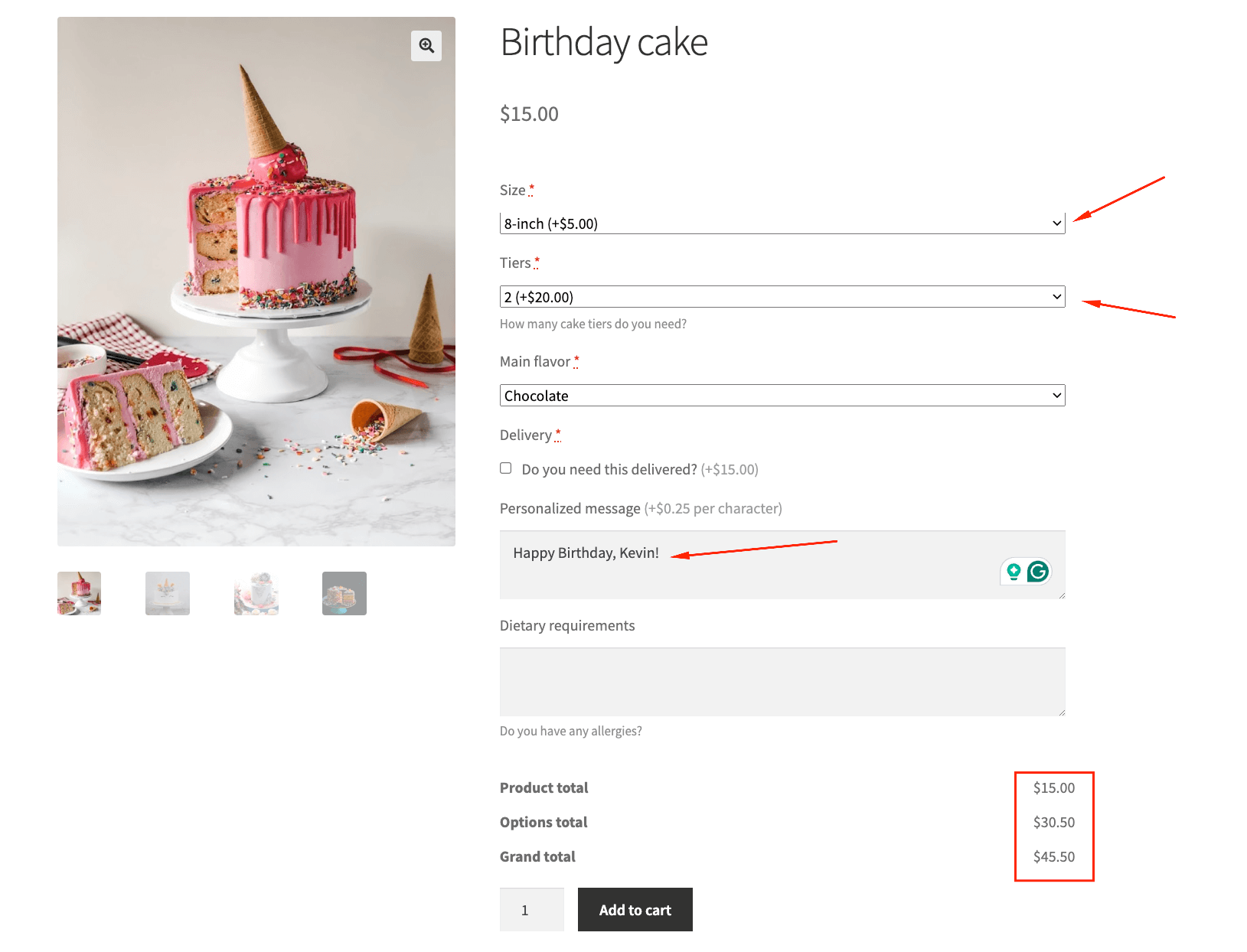
- Custom clothing with size, material, and design options
- Personalized gift boxes with product combination choices
- Business cards with text field customization
- Photo products requiring image uploads
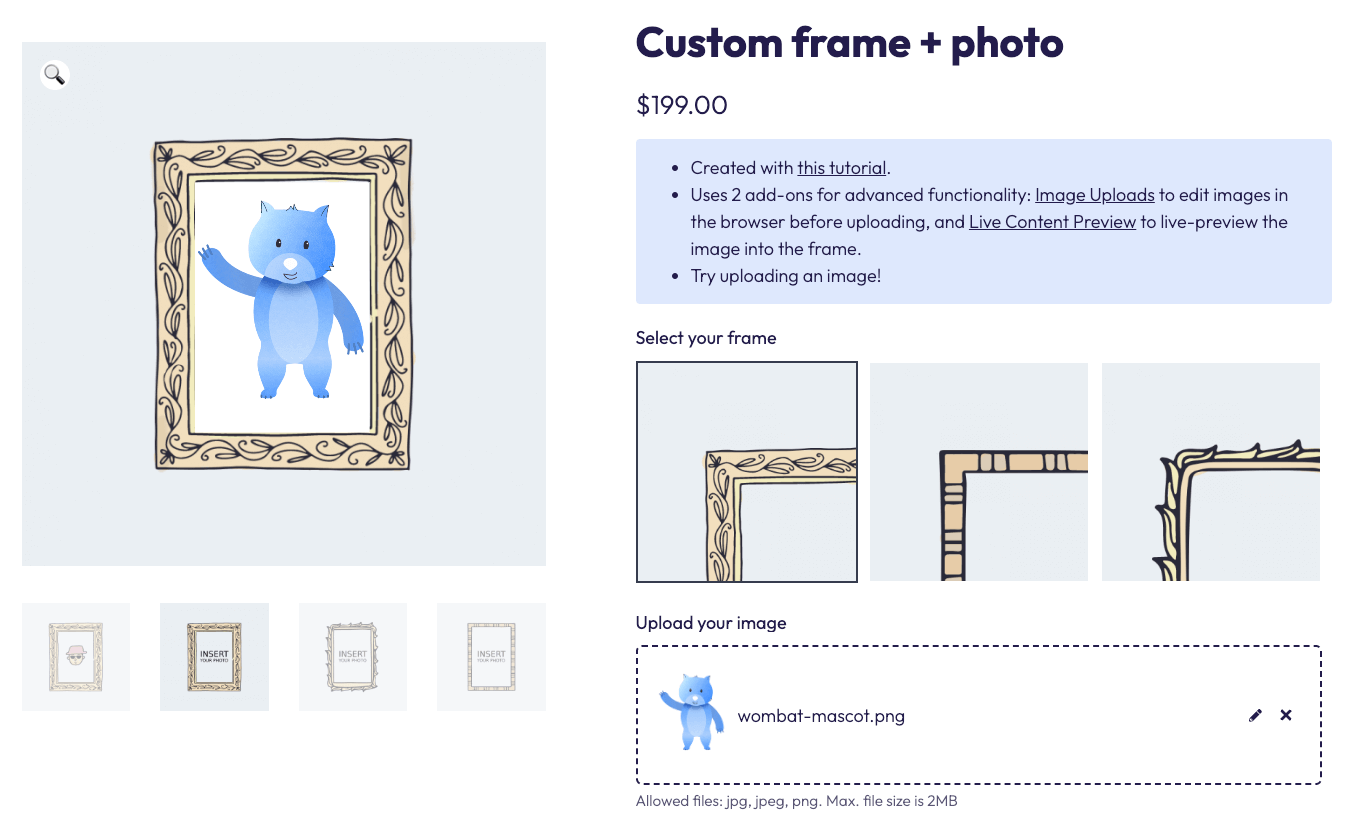
The flexibility of field-based customization allows merchants to match their online shopping experience to their unique products, ultimately creating more satisfied customers and reducing returns.
Pros and cons of customization
Pros:
- Unique offerings: Customized products help your store stand out from competitors by providing unique items tailored to individual preferences.
- Premium pricing: Customers are willing to pay more on average for products they can customize to their specifications.
- Higher satisfaction: When customers create their own product variations, they report greater satisfaction with their purchases.
- Reduced returns: Custom orders typically have lower return rates since customers have already committed to their specific choices.
Cons:
- Choice paralysis: Too many options can overwhelm customers, leading to abandoned shopping carts and purchase delays.
- Operational challenges: Processing custom orders requires additional steps and specialized workflows, extending production times.
- Inventory complications: Predicting which components will be needed becomes difficult with many customization options.
- Implementation costs: Setting up the necessary tools and interfaces requires initial investment in software and training.
Examples of personalization in e-commerce
Personalization in e-commerce goes far beyond simple product recommendations. Modern retailers employ sophisticated techniques to create tailored shopping experiences that feel custom-designed for each visitor.
- AI-driven predictive analytics anticipate customer needs before they even start shopping. By analyzing past purchase patterns, browsing behavior, and demographic data, these systems can predict what products a customer might need next. For example, an online grocery store might suggest reordering staple items as they’re about to run out based on typical usage patterns.
- Cross-device personalization creates seamless experiences regardless of how customers access your store. When a shopper browses products on their phone during their lunch break and later continues shopping on their laptop at home, cross-device personalization ensures they see the same recommendations and recently viewed items without starting over.
- Machine learning models optimize product sorting in ways impossible through manual curation. These systems analyze thousands of data points to present products most likely to appeal to each specific customer. Factors like past purchases, current trends, geographic location, and season all influence which products appear first in search results or category pages.
- Real-time personalization engines adapt content based on current browsing behavior. If a visitor suddenly shifts from browsing casual clothing to formal wear, the system quickly adjusts recommendations to match this new intent rather than relying solely on historical data.
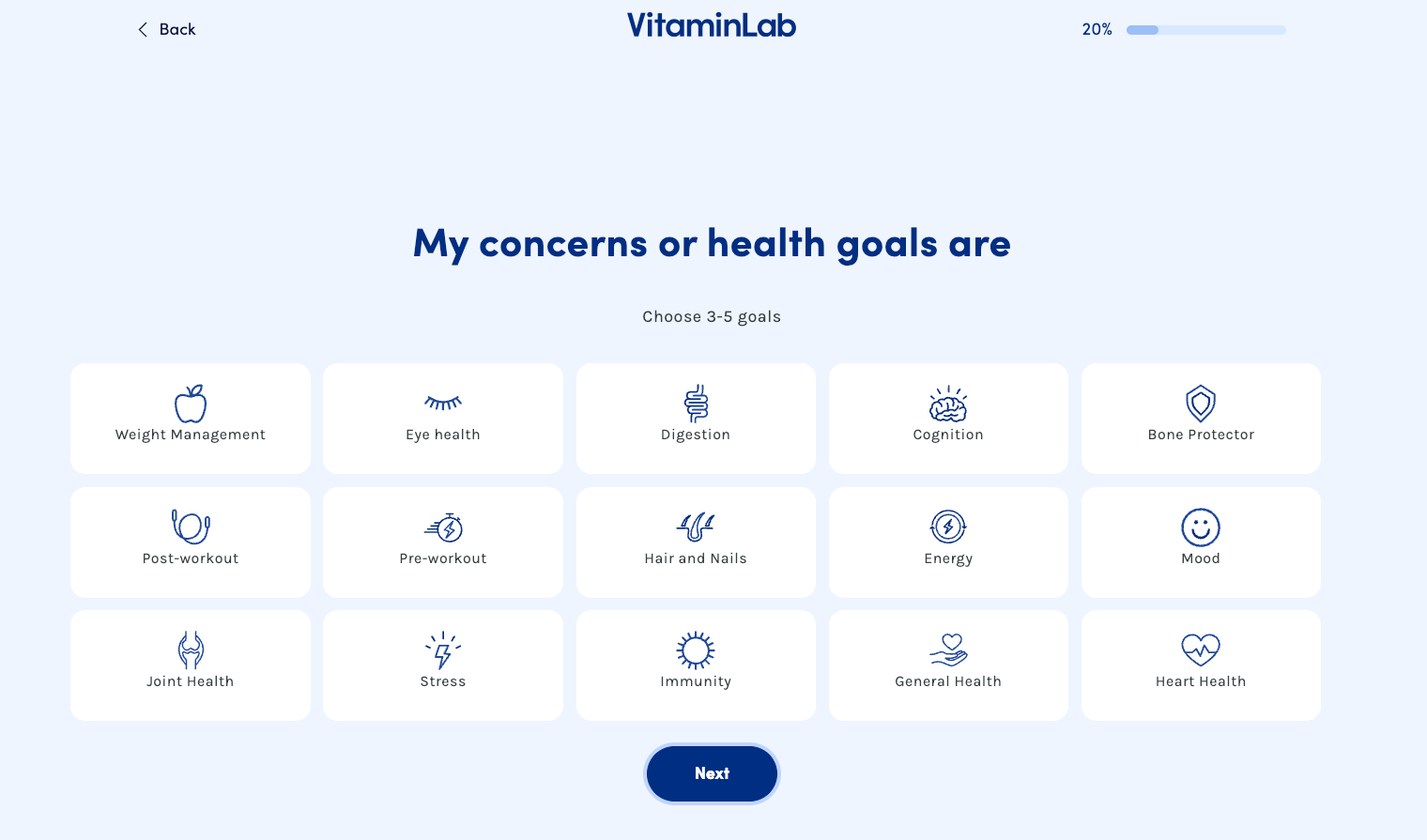
- Quiz-based personalization helps customers find exactly what they need through guided discovery. VitaminLab uses this approach by asking customers about their health goals, lifestyle, and current concerns to formulate custom vitamin recommendations tailored to their specific needs.
- Omnichannel personalization bridges online and physical retail experiences. Best Buy exemplifies this with their “Local Store Mode” feature that activates personalized notifications when customers enter physical stores. Their “On My Way” feature alerts store employees about incoming pickup orders, allowing staff to prepare items for a smooth handoff. This integration creates a cohesive brand experience regardless of how customers choose to shop.
These advanced personalization techniques transform standard online stores into intelligent shopping assistants that understand and anticipate customer needs.
Pros and cons of personalization
Pros:
- Revenue growth: According to Deloitte’s research, brands that excel in personalization exceed their revenue goals by nearly 10% on average, compared to brands with low personalization maturity.
- Higher conversion: Personalization leaders report 54% improvement in conversion rates compared to just 38% for low-maturity brands.
- Better engagement: Personalized experiences drive 61% higher customer engagement compared to traditional approaches.
- Customer loyalty: Personalization leaders are 71% more likely to report improved customer loyalty than companies with basic personalization.
Cons:
- Privacy requirements: Data collection demands strict compliance with regulations like GDPR and transparent privacy policies.
- Fine line to walk: The research shows a persistent gap – brands believe they personalize 61% of experiences, but consumers only recognize 43% as personalized.
- Technical demands: Implementing personalization requires specialized software and data infrastructure that can be costly.
- Testing burden: Ongoing experimentation and A/B testing are necessary to optimize personalization strategies, requiring dedicated resources.
Transform your WooCommerce customization ability today
The fundamental difference between these approaches is control: personalization puts algorithms in charge, while customization gives customers the freedom to create. Though both strategies boost engagement, they serve different purposes in your e-commerce strategy.
Adding customization to your WooCommerce store is remarkably simple with Advanced Product Fields. The plugin lets you create checkbox options, conditional fields, and text inputs without any coding knowledge. Even small businesses can quickly implement product customization to differentiate themselves from competitors offering standard products.
While personalization offers significant benefits, it requires substantial investment in data infrastructure and analysis tools. For smaller stores, the costs of implementing sophisticated personalization may initially outweigh the returns, making customization a more accessible starting point.
Ready to transform your store with customization options customers will love? Download Advanced Product Fields today and start offering the personalized shopping experience that builds customer loyalty and increases sales.